Syntax behind R programming
Working with R
R can be tricky to wrap your head around at first.
You must follow pretty specific syntax rules for it to work. It won’t guess for you.
- Case-sensitive interpreted language
- Enter commands at prompt
>or in batch - Statements consist of functions and assignments
- Comments are preceded by #
- semi-colons separate statements on a line
Some R code basics
<-is known as an “assignment operator” – it means “Make the object named to the left equal to the output of the code to the right”&means AND, in Boolean logic|means OR, in Boolean logic!means NOT, in Boolean logic- When referring to values entered as text, or to dates, put them in quote marks like this:
"United States", or"2016-07-26". Numbers are not quoted - When entering two or more values as a list, combine them using the function
c, for combine, with the values separated by commas, for exmaple:c:("2017-07-26", "2017-08-04") - As in a spreadsheet, you can specify a range of values with a colon, for example:
c(1:10)creates a list of integers (whole numbers) from one to ten. - Some common operators:
+-add, subtract*/multiply, divide><greater than less than>=<=greater than or equal to, less than or equal to!=not equal to
- Equal signs can be confusing
==tests whether the objects on either end are equal. This is often used in filtering data=makes an object equal to a value, which is similar to<-but used within a function.
- Handling null values:
- Nulls are designated as
NA is.na(x)looks for nulls within variablex.!is.na(x) looks for non-null values within variablex`
- Nulls are designated as
Here, is.na() is a function. Functions are followed by parentheses, and act on code/data in the parentheses.
Object and variable names in R should not contain spaces
This is what happens when you run the two lines below in the console.
In those code sections, the code preceeded by ## is the output of the code from the lines above.
x <- c(4,4,5,6,7,2,9)
length(x); mean(x)## [1] 7## [1] 5.285714plot(x)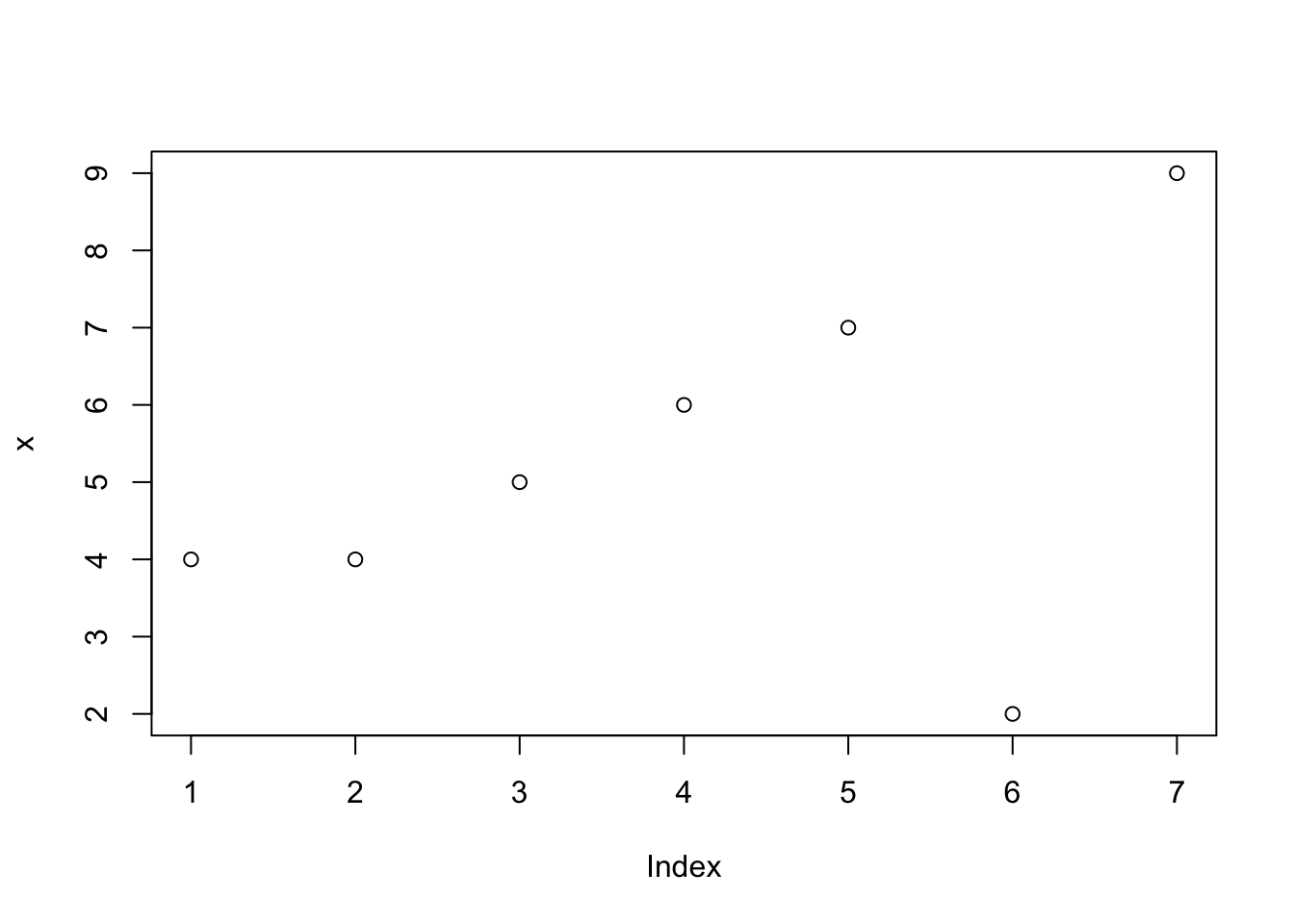
It first stored the array for c(4,4,5,6,2,9) into x
And the function length() as applied to x was length(x) and the output was 7. This function counted the numbers in the array x.
and then it was followed by the result of mean(x) which was 5.285715. That is the average of all the numbers in the x array.
And plot()?
That charted out the results– the x-axis was the position of the number in the array and the y-axis was the actual number.
Important points about R
- Everything is done through functions
- Functions manipulate objects
- An object is anything that can be assigned to a variable name
- Includes constants, data structures, functions, and even graphs
- All objects have a **class* - tells generic functions like
print(),plot(), andsummary()how to handle it. - Assignments are made with the
<-operator
R Workspace
- Your current R working environment
- Includes any user-defined objects (e.g. vectors, data frames, functions)
| Function | Action |
|---|---|
getwd() |
List current working directory |
setwd("mydirectory") |
Change the current working directory to mydirectory |
ls() |
List the objects in the current workspace |
rm(object) |
Delete object |
save(objectlist, file="myfile) |
Save specific objects to a file |
load("myfile") |
Load a workspace into the current session (default = .RData) |
Packages
- Collections of R functions, data, and compiled code in well-defined format
- Massively extend the functionality of R
- Thousands of user-written packages on CRAN
Mac users may need to alter their security preferences to allow apps authored by non-Apple developers to install. If you notice an error, try to change your system preferences.
Getting Help
| Function | Action |
|---|---|
help.start() |
General help |
help("foo") or ?foo |
Help on function foo (the quotation marks are optional) |
help.search("foo") or ??foo |
Search the help system for instances of the string foo |
example("foo") |
Examples of function foo (the quotation marks are optional) |
Working with Packages
- install.packages(“packagename”)
update.packages()
- library(packagename)
help(package=“packagename”)
- library() #what packages are in the library
search() #what packages are loaded
Common Mistakes
- Using the wrong case
- help(), Help(), and HELP() are three different functions (and only the first one will work)
- Forgetting to use quotation marks when they are needed
- install.packages(“gclus”) will work, while install.packages(gclus) will generate an error.
- Forgetting to include the parentheses in a function call
- help() rather than help. Even if there are no options, you still need the().
- Using the
\in a path name on Windows- R sees the backlash character as an escape character.
setwd("c:\mydata")will generate an error. Usesetwd("c:/mydata")orsetwd("c:\\mydata")instead
- Using a function from a package that is not loaded
- The function
str_trim()is contained in the stringr package. - If you try to use it before loading the package, you will get an error
- The function